Contents
This is the webpage of XAEM version 0.1.0. The most updated version of XAEM is here:
https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/xaem/
1. Introduction
2. Download and installation
3. XAEM: step by step instruction and explanation
3.1 Preparation for the annotation reference
3.2 Quantification of transcripts
4. A practical copy-paste example of running XAEM
5. Dataset for differential expression (DE) analysis
1. Introduction
This document shows how to use XAEM [Deng et al., 2019] to quantify isoform expression for multiple samples.
Software requirements for XAEM:
- R version 3.3.0 or later with installed packages: foreach and doParallel
- C++11 compliant compiler (g++ >= 4.7)
- XAEM is currently tested in Linux OS environment
Annotation reference: XAEM requires a fasta file of transcript sequences and a gtf file of transcript annotation. XAEM supports all kinds of reference and annotation for any species. In the XAEM paper, we use the UCSC hg19 annotation:
- Download the sequences of transcripts:transcripts.fa.gz
- Download the annotation of transcripts: genes_annotation.gtf.gz
- Download the design matrix X of this annotation: X_matrix.RData (X matrix is an essential object for bias correction and isoform quantification, see Section 4.1.2 for more details)
2. Download and installation
If you use the binary version of XAEM (recommended):
- Download the latest binary version from XAEM website:
wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/XAEM-binary-0.1.0.tar.gz
- Uncompress to folder
tar -xzvf XAEM-binary-0.1.0.tar.gz
- Move to the XAEM_home directory and do the configuration for XAEM
cd XAEM-binary-0.1.0 bash configure.sh
- Add paths of lib folder and bin folder to LD_LIBRARY_PATH and PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/path/to/XAEM-binary-0.1.0/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH export PATH=/path/to/XAEM-binary-0.1.0/bin:$PATH
If you want to build XAEM from sources:
- Download XAEM and move to XAEM_home directory
wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/XAEM-source-0.1.0.tar.gz tar -xzvf XAEM-source-0.1.0.tar.gz cd XAEM-source-0.1.0 bash configure.sh
- XAEM requires information of flags from Sailfish including DFETCH_BOOST, DBOOST_ROOT, DTBB_INSTALL_DIR and DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX. Please refer to the Sailfish website for more details of these flags.
- Do installation by the following command:
DBOOST_ROOT=/path/to/boostDir/ DTBB_INSTALL_DIR=/path/to/tbbDir/ DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/path/to/expectedBuildDir bash install.sh
- After the installation is finished, remember to add the paths of lib folder and bin folder to LD_LIBRARY_PATH and PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/path/to/expectedBuildDir/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH export PATH=/path/to/expectedBuildDir/bin:$PATH
Do not forget to replace “/path/to/” by your local path.
3. XAEM: step by step instruction and explanation
XAEM mainly contains the following steps:
- Preparation for the annotation reference: to process the annotation of transcripts to get essential information for transcript quantification. This step includes 1) index transcript sequences and 2) Construct the design matrix X.
- Quantification of transcripts: to get input from multiple RNA-seq samples to do quasi-mapping, generate data for quantifying transcript expression. This step consists of 1) generate equivalence class table; 2) create Y count matrix and 3) estimate transcript expression using AEM algorithm to update the X matrix and transcript (isoform) expression.
3.1 Preparation for the annotation reference
3.1.1 Indexing transcripts
Using TxIndexer to index the transcript sequences in the reference file (transcripts.fa). For example:
wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/transcripts.fa.gz gunzip transcripts.fa.gz TxIndexer -t /path/to/transcripts.fa -o /path/to/TxIndexer_idx
3.1.2 Construction of the X matrix (design matrix)
This step constructs the X matrix required by the XAEM pipeline. For users working with human annotation of UCSC hg19 the X matrix can be downloaded here: X_matrix.RData.
Given file transcripts.fa containing the transcript sequences of an annotation reference, we construct the design matrix as follows.
- a) Generate simulated RNA-seq data using the R-package “polyester”
## R-packages of "polyester" and "Biostrings" are required Rscript XAEM_home/R/genPolyesterSimulation.R /path/to/transcripts.fa /path/to/design_matrix
- b) Run GenTC to generate Transcript Cluster (TC) using the simulated data. GenTC will generate an eqClass.txt file as the input for next step.
GenTC -i /path/to/TxIndexer_idx -l IU -1 /path/to/design_matrix/sample_01_1.fasta -2 /path/to/design_matrix/sample_01_2.fasta -p 8 -o /path/to/design_matrix
- c) Create a design matrix using buildCRP.R. The parameter setting for this function is as follows.
- in: the input file (eqClass.txt) obtained from the last step.
- out: the output file name (*.RData) which the design matrix will be saved.
- H: (default H=0.025) is the threshold to filter false positive neighbors in each X matrix. (Please refer to the XAEM paper, Section 2.2.1)
Rscript XAEM_home/R/buildCRP.R in=/path/to/design_matrix/eqClass.txt out=/path/to/design_matrix/X_matrix.RData H=0.025
3.2 Quantification of transcripts
Suppose we already created a working directory “XAEM_project” (/path/to/XAEM_project/) for quantification of transcripts.
3.2.1 Generating the equivalence class table
The command to generate equivalence class table for each sample is similar to “sailfish quant”. For example, we want to run XAEM for sample1 and sample2 with 4 cpus:
XAEM -i /path/to/TxIndexer_idx -l IU -1 s1_read1.fasta -2 s1_read2.fasta -p 4 -o /path/to/XAEM_project/sample1 XAEM -i /path/to/TxIndexer_idx -l IU -1 s2_read1.fasta -2 s2_read2.fasta -p 4 -o /path/to/XAEM_project/sample2
- If the data is compressed in gz format. We can combine with gunzip for a decompression on-fly:
XAEM -i /path/to/TxIndexer_idx -l IU -1 <(gunzip -c s1_read1.gz) -2 <(gunzip -c s1_read2.gz) -p 4 -o /path/to/XAEM_project/sample1 XAEM -i /path/to/TxIndexer_idx -l IU -1 <(gunzip -c s2_read1.gz) -2 <(gunzip -c s2_read2.gz) -p 4 -o /path/to/XAEM_project/sample2
3.2.2 Creating Y count matrix
After running XAEM there will be the output of the equivalence class table for multiple samples. We then create the Y count matrix. For example, if we want to run XAEM parallelly using 8 cores, the command is:
Rscript Create_count_matrix.R workdir=/path/to/XAEM_project core=8
3.2.3 Updating the X matrix and transcript expression using AEM algorithm
When finish the construction of Y count matrix, we use the AEM algorithm to update the X matrix. The updated X matrix is then used to estimate the transcript (isoform) expression. The command is as follows.
Rscript AEM_update_X_beta.R workdir=/path/to/XAEM_project core=8 design.matrix=X_matrix.RData isoform.out=XAEM_isoform_expression.RData paralog.out=XAEM_paralog_expression.RData merge.paralogs=FALSE isoform.method=average remove.ycount=TRUE
Parameter setting
- workdir: the path to working directory
- core: the number of cpu cores for parallel computing
- design.matrix: the path to the design matrix
- isoform.out (default=XAEM_isoform_expression.RData): the output contains the estimated expression of individual transcripts, where the paralogs are split into separate isoforms. This file contains two objects: isoform_count and isoform_tpm for estimated counts and normalized values (TPM). The expression of the individual isoforms is calculated with the corresponding setting of parameter “isoform.method” below.
- isoform.method (default=average): to report the expression of the individual members of a paralog as (i) average (default) or (ii) total from the expression of the paralog set.
- paralog.out (default=XAEM_paralog_expression.RData): the output contains the estimated expression of merged paralogs. This file consists of two objects: XAEM_count and XAEM_tpm for the estimated counts and normalized values (TPM).
- merge.paralogs (default=FALSE) (*): the parameter to turn on/off (value=TRUE/FALSE) the paralog merging in XAEM. The default is off, which will generate the same set of isoforms between different projects. To turn it on, just add “merge.paralogs=TRUE”.
- remove.ycount (default=TRUE): to clean all data of Ycount after use.
The output in this step will be saved in XAEM_isoform_expression.RData, which is the TPM value and raw read counts of multiple samples.
Note: (*) In XAEM pipeline we provide this parameter (merge.paralog) to merge or not merge the paralogs within the updated X matrix (please see XAEM paper Section 2.2.3 and Section 2.3). Turning on the paralog merging step produces a more accurate estimation. Turning off this step (default) can produce the same sets of isoforms between different projects.
4. A practical copy-paste example of running XAEM
This section presents a tutorial to run XAEM pipeline with a toy example. Suppose that input data contain two RNA-seq samples and server supplies 4CPUs for computation. We can test XAEM by just copy and paste of the example commands.
- Download the binary version of XAEM and do configuration
# Create a working folder mkdir XAEM_example cd XAEM_example # Download the binary version of XAEM wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/XAEM-binary-0.1.0.tar.gz # Configure the tool tar -xzvf XAEM-binary-0.1.0.tar.gz cd XAEM-binary-0.1.0 bash configure.sh # Add the paths to system export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$PWD/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH export PATH=$PWD/bin:$PATH cd ..
- Download annotation files and index the transcripts
## download annotation files # Download the design matrix for the human UCSC hg19 annotation wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/X_matrix.RData # Download the fasta of transcripts in the human UCSC hg19 annotation wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/transcripts.fa.gz gunzip transcripts.fa.gz ## Run XAEM indexer TxIndexer -t transcripts.fa -o TxIndexer_idx
- Download the RNA-seq data of two samples: sample1 and sample2
## Download input RNA-seq samples # Create a XAEM project to save the data mkdir XAEM_project cd XAEM_project # Download the RNA-seq data wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/sample1_read1.fasta.gz wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/sample1_read2.fasta.gz wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/sample2_read1.fasta.gz wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/sample2_read2.fasta.gz cd ..
- Generate the equivalence class tables for these samples
# Number of CPUs CPUNUM=4 # Process for sample 1 XAEM -i TxIndexer_idx -l IU -1 <(gunzip -c XAEM_project/sample1_read1.fasta.gz) -2 <(gunzip -c XAEM_project/sample1_read2.fasta.gz) -p $CPUNUM -o XAEM_project/sample1 # Process for sample 2 XAEM -i TxIndexer_idx -l IU -1 <(gunzip -c XAEM_project/sample2_read1.fasta.gz) -2 <(gunzip -c XAEM_project/sample2_read2.fasta.gz) -p $CPUNUM -o XAEM_project/sample2
- Create Y count matrix
# Note: R packages "foreach" and "doParallel" are required for parallel computing Rscript $PWD/XAEM-binary-0.1.0/R/Create_count_matrix.R workdir=$PWD/XAEM_project core=$CPUNUM design.matrix=$PWD/X_matrix.RData
- Estimate isoform expression using AEM algorithm
Rscript $PWD/XAEM-binary-0.1.0/R/AEM_update_X_beta.R workdir=$PWD/XAEM_project core=$CPUNUM design.matrix=$PWD/X_matrix.RData isoform.out=XAEM_isoform_expression.RData paralog.out=XAEM_paralog_expression.RData
The outputs are stored in the folder of “XAEM_project” including XAEM_isoform_expression.RData and XAEM_paralog_expression.RData.
5. Dataset for differential expression (DE) analysis
In XAEM paper we have used the RNA-seq data from the breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB-231) for DE analysis. Since the original data was generated by our collaborators and not published yet, we provide the equivalence class table by running the read-alignment tool Rapmap, which is the same mapper of Salmon and totally independent from XAEM algorithm. We also prepare the R scripts and the guide to replicate the DE analysis results in the paper.
In this section, we present an instruction to download the data and run the scripts. We try to build the pipeline following the copy-paste manner in shell, but the part of R scripts must be run in R console.
5.1 Download the R-scripts and the design matrix
This step is to download the R-scripts, change directory to the folder containing the R-scripts and download the design matrix.
# Download R-scripts
wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/brca_singlecell/RDR_brca_singlecell.zip unzip RDR_brca_singlecell.zip cd RDR_brca_singlecell
# Download the design matrix
wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/X_matrix.RData
5.2 Run XAEM from the equivalence class tables which are the output of read-alignment tool Rapmap
Download the data of equivalence classes
# Download the table of equivalence classes of the single cells which are the output of read-alignment tool Rapmap
wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/brca_singlecell/brca_singlecell_eqclassDir.zip
unzip brca_singlecell_eqclassDir.zip
Run XAEM with the input from the equivalence class table using the R-codes below. Note: This step takes about 2 hours using a personal computer with 4 CPUs. Users can consider skipping this step and downloading the available XAEM results for the downstream analysis.
# set the project path
projPath=getwd();
setwd(projPath)
source("collectDataOfXAEM.R")
If users want to download the available XAEM results
# Download the available results of XAEM
wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/brca_singlecell/XAEM_results.zip
unzip XAEM_results.zip
5.3 Differential-expression analysis of XAEM and other methods
Download the data of cufflinks and salmon. These files contain the read-count data of methods with and without using bias correction.
# Download the results of cufflinks
wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/brca_singlecell/cufflinks_results.zip
unzip cufflinks_results.zip
# Download the results of salmons
wget https://www.meb.ki.se/sites/biostatwiki/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/XAEM_datasources/brca_singlecell/salmon_results.zip
unzip salmon_results.zip
Run the codes below in R to do normalization and differential expression analysis.
# set the project path
projPath=getwd();
setwd(projPath)
# Normalize the data of three methods XAEM, Salmon and Cufflinks
source("Isoform_Expression_CPM_Normalization.R")
# Do DE analysis and plot figures
source("DEanalysis_plots.R")
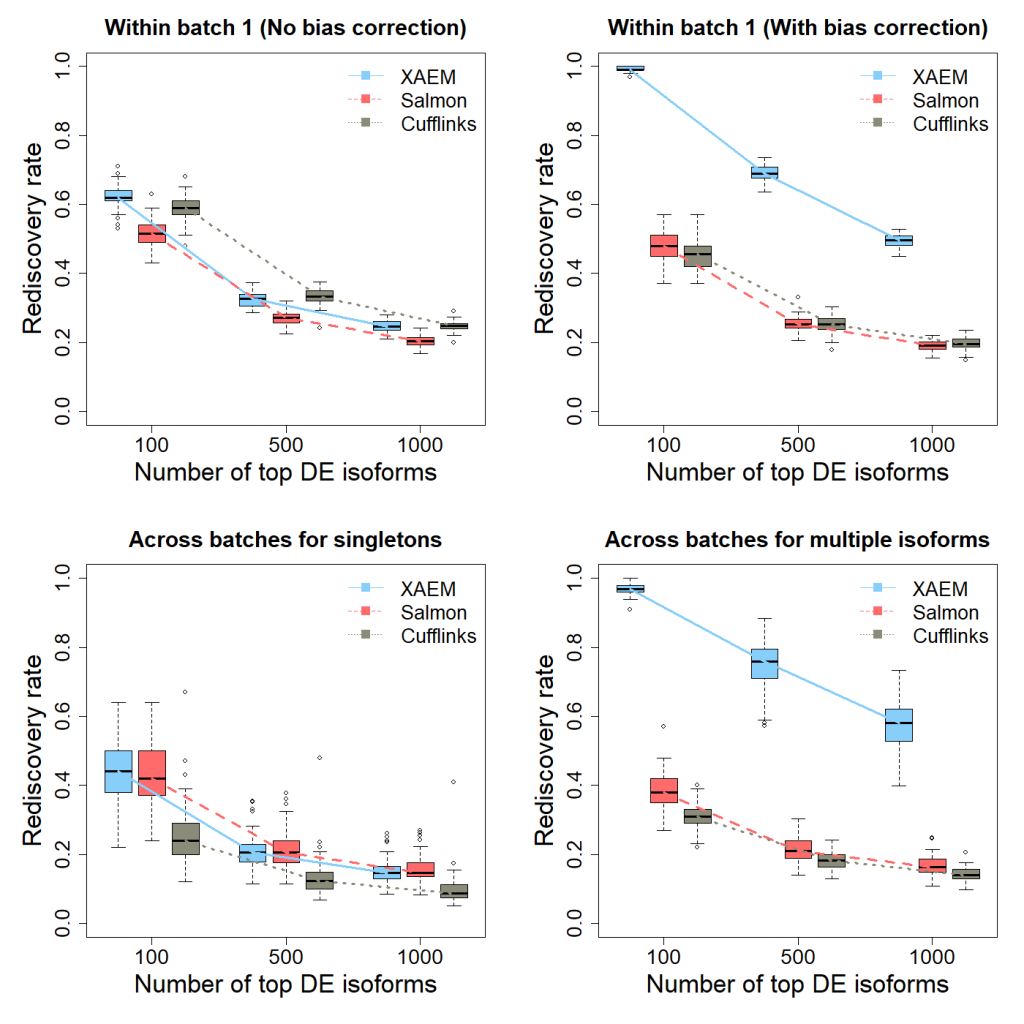
# output: DE_Analysis.png
The results of the differential expression analysis (Figure 1 below) are the plots (DE_Analysis.png) reproducing Figure 3 of the XAEM paper. Note that due to the randomness of 50 times’ run, the figure might be slightly different from the figure in the paper.
References:
- Deng, Wenjiang, Tian Mou, Nifang Niu, Liewei Wang, Yudi Pawitan, and Trung Nghia Vu. 2019. “Alternating EM Algorithm for a Bilinear Model in Isoform Quantification from RNA-Seq Data.” Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz640.